College Catalog: 2014-2015
School of Theoretical and Applied Science (TAS): Computer Science (B.S.)
Website: School of Theoretical and Applied Science
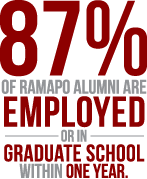
Computers are pervasive in today’s world and Ramapo College Computer Science graduates have available to them a broad range of career opportunities in business, government, and academia. Our recent graduates have established careers in software development, project management, research, marketing, database development and administration, financial engineering, data mining, systems administration, quality assurance, education, game development, management, consulting and sales. Our students often continue on to graduate school.
Computer Science is the study of the representation, storage, and transformation of information. The subject areas of computer science include algorithms and data structures, programming languages, object oriented programming, GUI programming, web based development, operating systems, compiler design, numerical analysis, simulation, data communication and network programming, database design, artificial intelligence, computer graphics, security, and software methodologies.
This broad body of knowledge is presented in a manner which encourages Computer Science majors to develop professional competence, and acquire intellectual maturity and curiosity; establishing a long-term commitment to remain current in this rapidly changing discipline. Indeed, the Computer Science major at the College is in a continual state of evolution, with new courses being added to the program and every course in the major being regularly updated. The Program has an Advanced Topics course to facilitate the rapid introduction of new material into the major.
The Computer Science major at Ramapo is based on the philosophy that true learning occurs through active participation. This notion is incorporated throughout the curriculum. For example, all the courses in the major require programming projects that illustrate and expand the course content. Before completing the major, students must design and implement a significant piece of software as their senior project. Additionally, Computer Science students are encouraged to participate in one of the many experiential learning opportunities available through off-campus internships.
The Computer Science faculty brings a wide diversity of experience in industry and academia. Computer networking, object oriented programming, financial modeling, database design, web development, UNIX, .NET and Windows programming, artificial intelligence, virtual reality, GUI programming, software methodologies, programming languages, numerical analysis and computer graphics are areas well represented by the faculty.
- Transfer students who have 48 or more credits accepted at the time of transfer are waived from the courses marked with a (W) below. Waivers only apply to General Education Requirements NOT School Core or Major Requirements.
- Double counting between General Education, School Core, and Major may be possible. Check with your advisor to see if any apply.
- Writing Intensive Requirement (six courses): three writing intensive courses in the general education curriculum are required: First Year Seminar, Critical Reading and Writing, and Readings in the Humanities; the other three courses are taken in the major.
- Not all courses are offered each semester. Please check the current Schedule of Classes for semester course offerings.
COMPUTER SCIENCE MAJOR
- Subject & Course # – Title & Course Description
- GENERAL EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS
- INTD 101 - FIRST YEAR SEMINAR (W)
- SELECT ONE – (W) BADM 115 - PERSPECTIVES OF BUSINESS AND SOCIETY OR
- (W) SOSC 101 - SOCIAL ISSUES
- CRWT 102 - CRITICAL READING & WRITING II
- AIID 201 - READINGS IN THE HUMANITIES (W)
- SELECT ONE – (W) GE-HISTORY CATEGORY: HIST 101-110
- SELECT ONE – GE-INTERCULTURAL NORTH AMERICA CATEGORY
- SELECT ONE – GE-INTERNATIONAL ISSUES CATEGORY
- SELECT ONE – (W) GE-TOPICS ARTS AND HUMANITIES CATEGORY OR
- (W) GE-TOPICS SOCIAL SCIENCE CATEGORY
- SCHOOL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED SCIENCE REQUIREMENT
- SCIENCE IN A CULTURAL PERSPECTIVE COURSE:
- SCIN 230 - COMPUTERS AND SOCIETY
- COMPUTER SCIENCE MAJOR REQUIREMENTS
- CMPS 147 - COMPUTER SCIENCE I
- CMPS 148 - COMPUTER SCIENCE II
- CMPS 220 - ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 231 - DATA STRUCTURES
- CMPS 311 - OPERATING SYSTEMS
- CMPS 361 - SOFTWARE DESIGN
- CMPS 366 - ORGANIZATION OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
- CMPS 450 - SENIOR PROJECT
- MATH 121 - CALCULUS I
- MATH 237 - DISCRETE STRUCTURES OR
- MATH 205 - MATHEMATICAL STRUCTURES
- MATHEMATICS ELECTIVES: SELECT TWO
- Note: must have MATH 121 Calculus I as a prerequisite.
- COMPUTER SCIENCE ELECTIVES: SELECT SEVEN
- CMPS 315 - THE UNIX ENVIRONMENT
- CMPS 316 - ADVANCED UNIX PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 327 - NETWORK PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 331 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- CMPS 342 - COMPUTER GRAPHICS
- CMPS 345 - ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
- CMPS 350 - FINANCIAL MODELING
- CMPS 357 - THE .NET ENVIRONMENT
- CMPS 364 - DATABASE DESIGN
- CMPS 367 - ADVANCED TOPICS:
- CMPS 369 - WEB APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
- CMPS 373 - OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 410 -
Note: A 2.0 GPA in the major is required for graduation.
- At least 1/2 of the courses fulfilling a minor must be distinct from the student’s major. That is, three of the five courses required for a minor cannot be used towards fulfillment of major requirements. A school core does not need to be completed for a minor. Minors are open to students regardless of school affiliation.
COMPUTER SCIENCE MINOR
- Subject & Course # – Title & Course Description
- REQUIRED COURSES:
- CMPS 147 - COMPUTER SCIENCE I
- CMPS 148 - COMPUTER SCIENCE II
- CMPS 231 - DATA STRUCTURES
- ELECTIVES: SELECT THREE
- CMPS 311 - OPERATING SYSTEMS
- CMPS 315 - THE UNIX ENVIRONMENT
- CMPS 316 - ADVANCED UNIX PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 327 - NETWORK PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 331 - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- CMPS 342 - COMPUTER GRAPHICS
- CMPS 345 - ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
- CMPS 350 - FINANCIAL MODELING
- CMPS 357 - THE .NET ENVIRONMENT
- CMPS 361 - SOFTWARE DESIGN
- CMPS 364 - DATABASE DESIGN
- CMPS 366 - ORGANIZATION OF PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
- CMPS 367 - ADVANCED TOPICS:
- CMPS 369 - WEB APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
- CMPS 373 - OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
- CMPS 410 -
- MATH 237 - DISCRETE STRUCTURES OR
- MATH 205 - MATHEMATICAL STRUCTURES
General Education Requirements
Four Year Plan
Graduation Requirements
School of Theoretical and Applied Science Website
Faculty Profiles